PTFE-Chambers - Measurement of Volatiles and Reactive Gases

PTFE Gas & Volatile Flux Chambers. Experimentation on highly reactive molecules in the atmosphere requires specific chambers. Teflon chambers (PTFE Chambers) are often used for studies on volatiles and reactive gases because they are relatively chemically inert. PTFE-reaction chambers are thus ubiquitous in studies of atmospheric chemistry.
Teflon Chambers for Experimentation on Reactive Gases and Volatiles

TC-400 Teflon Flux Chamber, to study interactions between Ozone, BVOC emissions and plant physiological status. The chamber was developed for the project UOZONE of the University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Vienna (BOKU). In brief, all mounting and side parts in contact with the air inside the 40 l plant chamber / reaction chamber are made from Teflon (PTFE). Plants are housed in PET bags. While potential interaction between vapour and PTFE-chamber walls can lead to the underestimation of some compounds, particular for least volatile compounds, the extent of prior use has been reported not to affect the sorption behaviour of Teflon (Zhang et al. 2015) - making the use of Teflon respiration chambers the preferred choice.
PTFE-Chamber - Specification
The TC-400 chamber design is freely configurable to meet the needs of your planned experiments, in particular to meet your target plant size (crown volume) and measured compounds. For example, we can adjust at your request:
- diameter of the reaction chambers` PTFE bottom (standard: 400 mm), size / location of the plant insertion point (Teflon-coated rubber), and numbers of air outlets realized in the bottom plate,
- height of air inlet in chamber (standard: 500 mm), and location of air entry point(s) (standard: on top, with diffusor),
- height of the table (fixed height or adjustable), on wheels or legs, no table etc.
In general, an "inversed design", targeting e.g. BVOC emissions by roots and microbiomes, is conceivable. We are happy to discuss your bespoke Teflon chamber configuration needs in person - adapting it to successfully measure the reactive molecules of your choice. If required, we can source valves, mass flow controllers, activated C filters, and tubing etc. for your experimental set-up.
| References | TC-400 PTFE Chamber | OPEN |
|
||
BVOC Chamber Set-up - Example
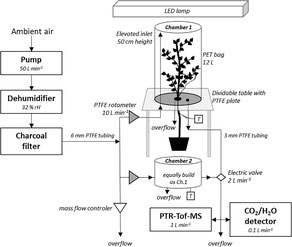
Setup of an experiment using the VSI TC-400 VOC chambers, as used by Fitzky et al. (2021), Frontiers in Plant Sciences.
Ambient air was flushed through a dehumidifier (32% rH) and the charcoal filter (see above for pictures) for providing close-to VOC-free air. The incoming air was entering each TC-400 chamber through an elevated inlet covered by Teflon tape. A mass flow controller was regulating the incoming air pressure. The PTFE-covered table of the TC-400 was dividable, allowing for tree stem insertion, and sealed with a PTFE-coated silicon stopper. A tree was inserted into measurement chambers, whereas a "control" chamber remained empty for parallel VOC background measurements. Up to four chambers were operated in parallel, with one always serving as "blank". A thermocouple (T) was installed at all chambers to monitor leaf / air temperature. A PET-bag was placed over the bottom plate and sealed. Two outlets in the bottom of the PTFE plates of each chamber were used as overflow and for gas analysis by the PTR-TOF-MS and CO2/H2O detector, respectively. See “Materials and Methods” for details, and Supplementary Figure 1 and above for images of the chamber in use.
| References |
Chambers for VOCS, BVOCs and Ozone Measurements |
OPEN |
|
||
For switching between PFTE chambers in open flow mode, effective gas multiplexing systems are available. See also Gas Pumps,Gas Flow Monitors, Pressure Sensors and Regulators, ...
For parallel measurement of CO2 and O2 in the chambers with a single analyser, consider the Q-S159 CO2 / O2 analyser. Various other Gas Analysing Systems are available.
See ecosystem and mesocosm respiration chambers for plant experiments measuring less reactive gases such as CO2 and O2.










